Enabling RDP Access to Azure Instances
Enabling RDP access is often, and probably should be, a last resort for debugging Azure instance weirdness. If for no other reason that it can be prone to external attack and security issues.
With that in mind, here's how to enable it in a Cloud Service:
- Add an import for RemoteAccess to each role.
- Add an import for RemoteForwarder to one role (you will get an obscure error if you add it to more than one.
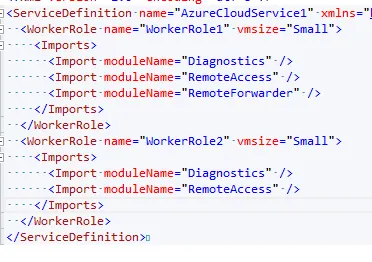
- Add settings for RemoteAccess to each role, making sure that the account expiration is something sensible (not christmas or new year's day :).
- Add a final setting to enable the RemoteForwarder.
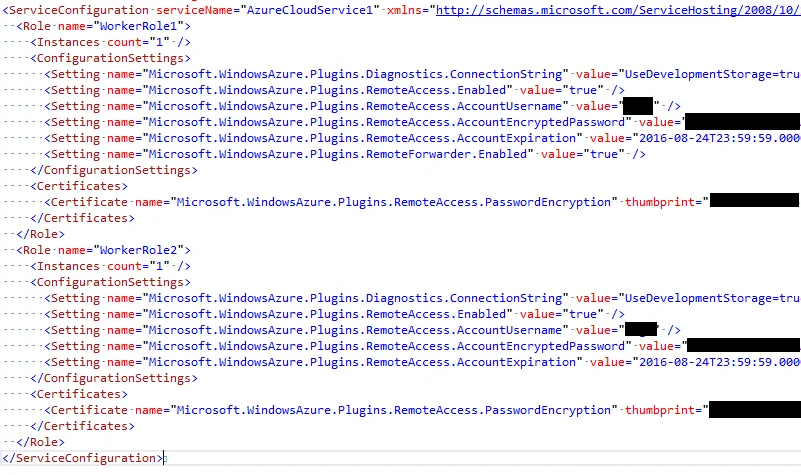
Despite it's slightly cryptic name, the RemoteForwarder is particularly important. It needs to be present and enabled on one role only so that RDP will work across any of the roles. The remote forwarder is used as a gateway for RDP to tunnel to a role instance so without it RDP will fail when you try to connect with a not very helpful "unable to connect" error.
The RemoteAccess setting needs to be enabled across all roles that require it.